Species Relationships: Symbiosis
Classical Symbiotic Relationships – Mutualism, Commensalism and Parasitism




Common Terms
- Interspecific interactions: Interactions between organisms of different species (deer and cattle).
- Intraspecific interactions: Interactions between members of the same species (interactions within a deer population).
- Mutualism: a relationship between two species of organisms in which both benefit from the association.
- Commensalism: A symbiotic relationship between two organisms of different species in which one derives some benefit while the other is unaffected.
- Parasitism: A symbiotic relationship in which one organism (the parasite) benefits and the other (the host) is harmed. Parasites derive nutrition from their host and may also gain other benefits such as shelter and a habitat in which to grow and reproduce.
- Endoparasites: A parasite, such as a tapeworm, that lives within another organism.
- Ectoparasites: A parasite, such as a flea, that lives on the exterior of another organism
Last week in lab we looked at Lichens.
What’s in a Lichen? How Scientists Got it Wrong for 150 years.
Mutualism in Some Carnivorous Plants
The Living, Breathing World of Borneos Carnivorous Pitcher Plants – wonderful pictures
Symbiotic Pollination Strategies
- Sexual Encounters of the Floral Kind – a few videoclips, some shown in lab
- The Fig Wasp and Fig Fruit – Short video showing the life cycle, narrated by David Attenborough
- NCSU Researcher studying Insect/Butterfly Wings Key to Flame Azalea Pollination
- NCSU Researcher studying 4 of North Carolina’s Oddest Pollinators (They Aren’t Bees)
- NCSU Researchers studying Climate Change and Critical Pollinators (Sept 2017)
- NCSU Pollinators Welcome Here
- Moths Work the Pollination Night Shift – short Smithsonian article
- UV Photography and flowers – National Geographraphic
- Hemp Fields Offer a Late Season Pollen Source for Stressed Bees (usually wind pollinated)
- A Brazilian tree that rains nectar to attract bat pollinators
Endosymbiotic Relationships – What do termites and cows have in common?

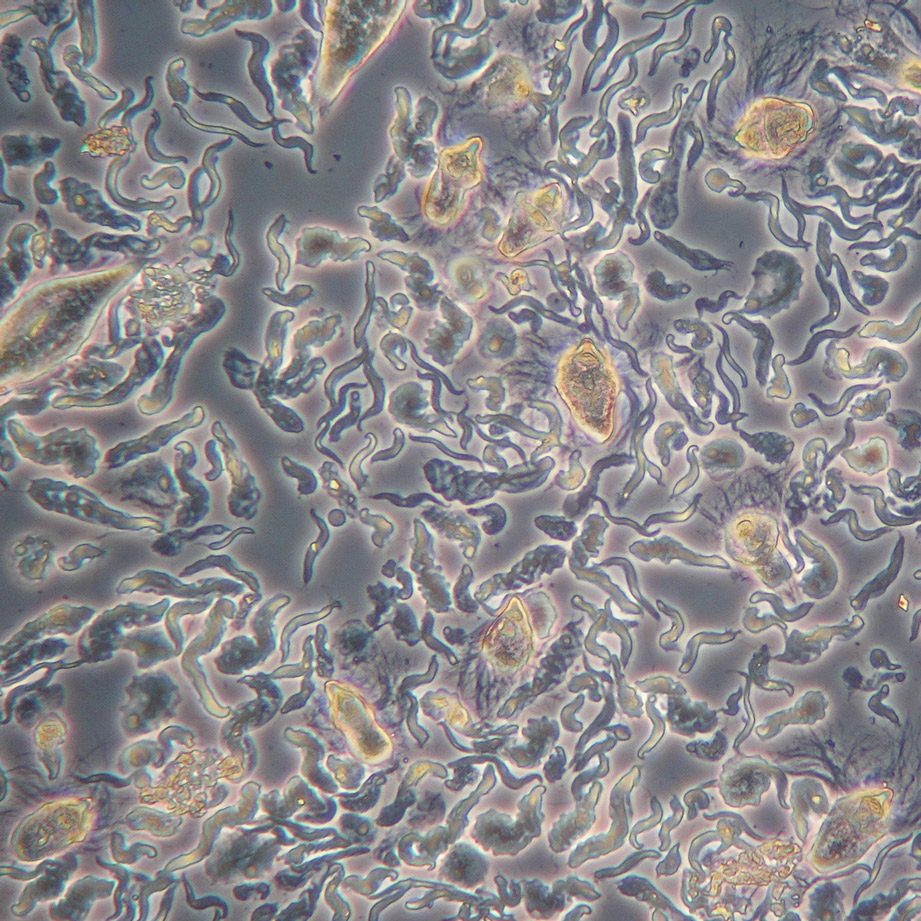
- Termite Gut Microbes – short video clip.
- Termite Gut Microbes – images of a variety of microbes Univ. of Conn. research lab.
- Microbial Symbiosis in Cow Rumen – ppt
- Cow rumen fluid – videoclip
- Pandas – another example of the importance of bacteria endosymbiosis – Short article about using genes from bacteria found in Panda feces and inserting them into yeast to increase biofuel efficiency. You will learn more about this technology in BIO 183 labs.
Parasitic Relationships
[callout heading=”Parasites Webquest Assignment” headingicon=”noicon” url=”https://wordpress-projects.wolfware.ncsu.edu/bio-181l-zchxzbn/laboratory-units/laboratory-7/parasites-webquest-assignment/” type=”basic” bgcolor=”huntyellow” /]
- Fish parasites with Mike Rowe (Dirty Jobs) and Dr. Rob Dunn (NCSU Applied Ecology Dept.) (1:57)
- Extended episode – “World’s Dirtiest Man” with Mike Rowe and Dr. Rob Dunn (41:30)
Fish Dissection:
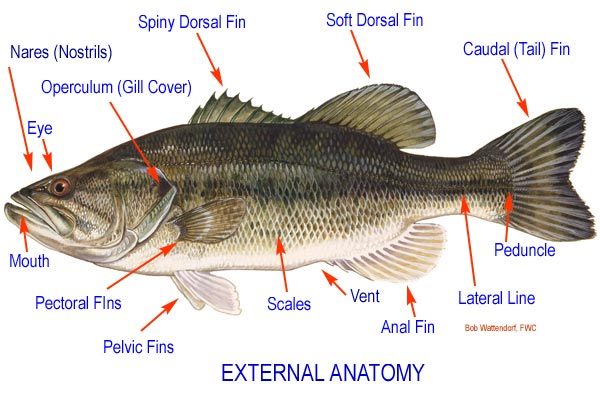
External Anatomy
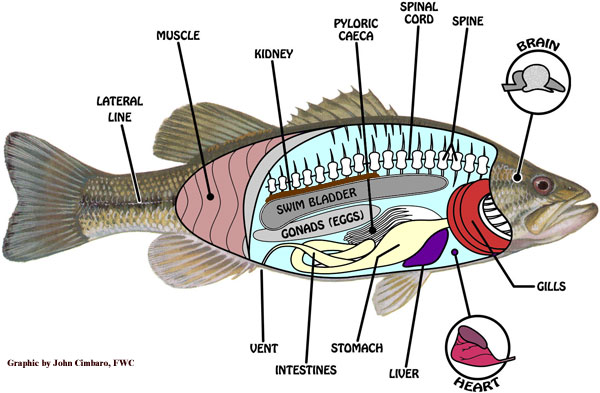
Internal Anatomy
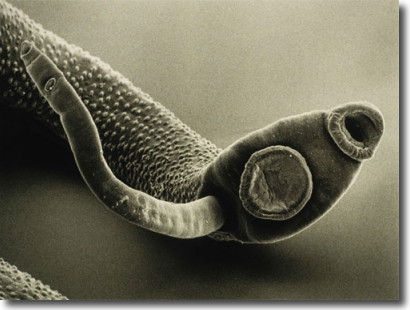
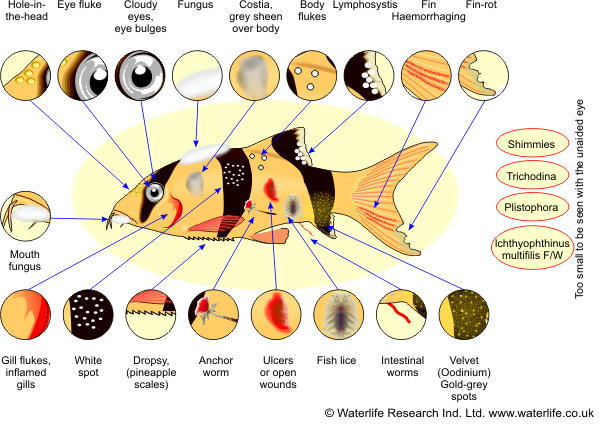
Common Fish Parasites/Diseases
Fish Parasites Collected in Lab
Fish Liver Flukes (metacercaria stage of life cycle–top four images):
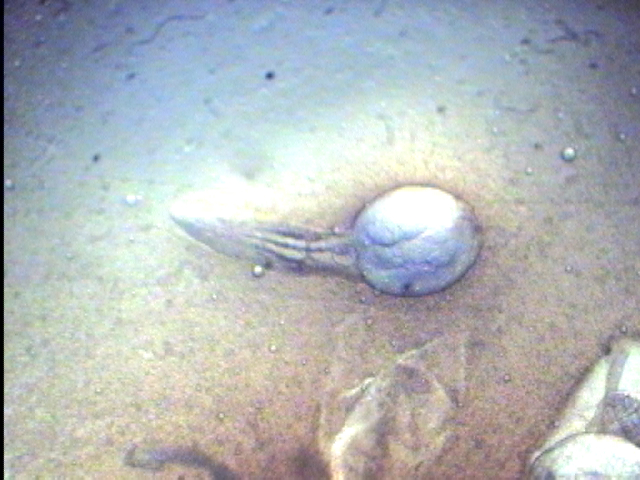
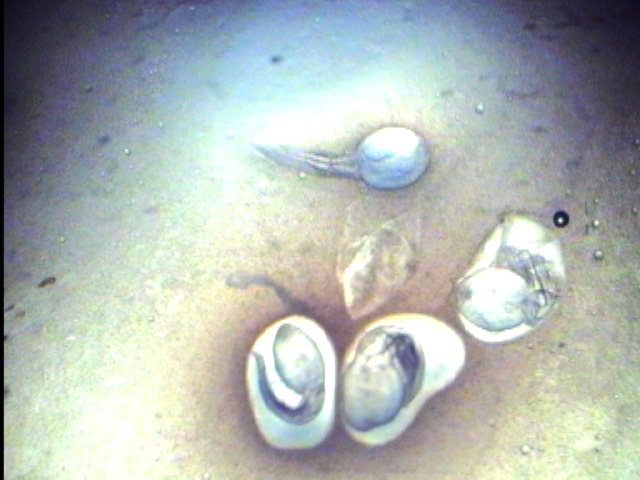
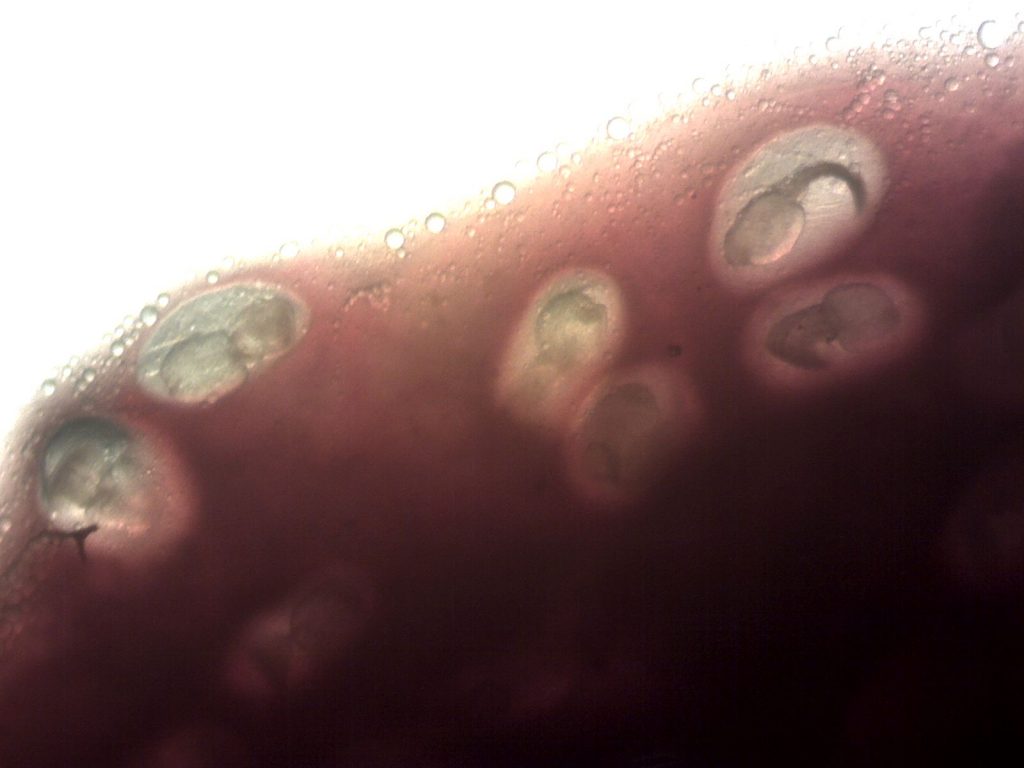

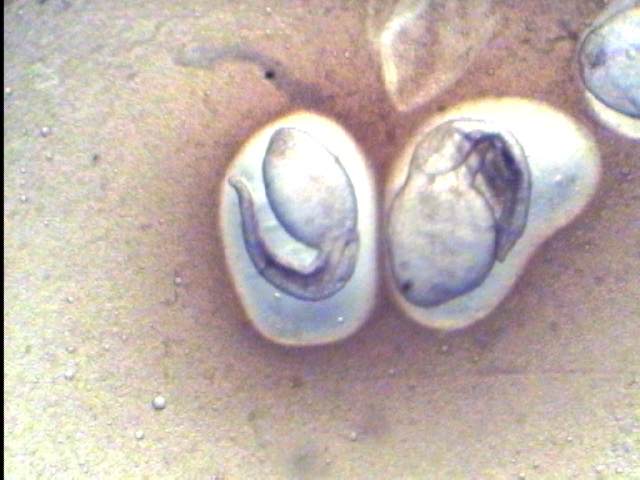
Flukes below were found growing on an infected fish heart (metacercaria stage):
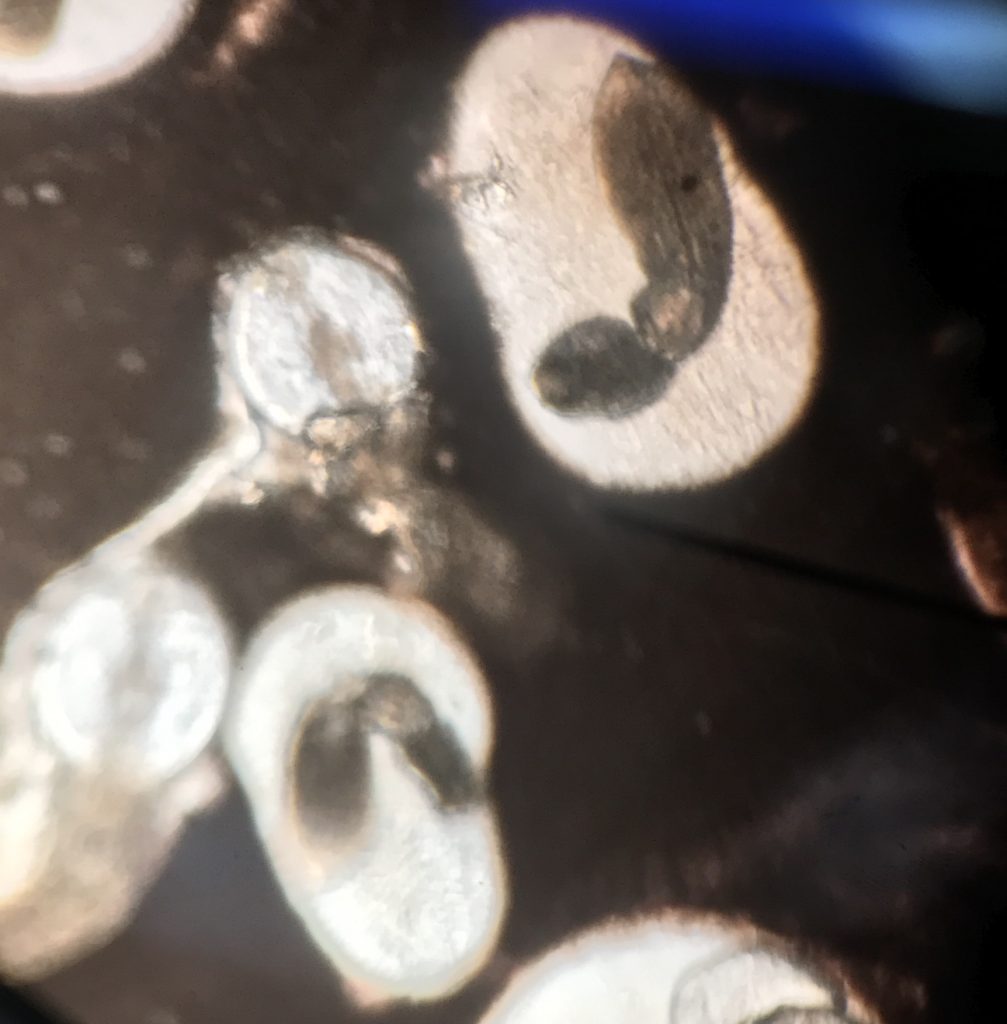

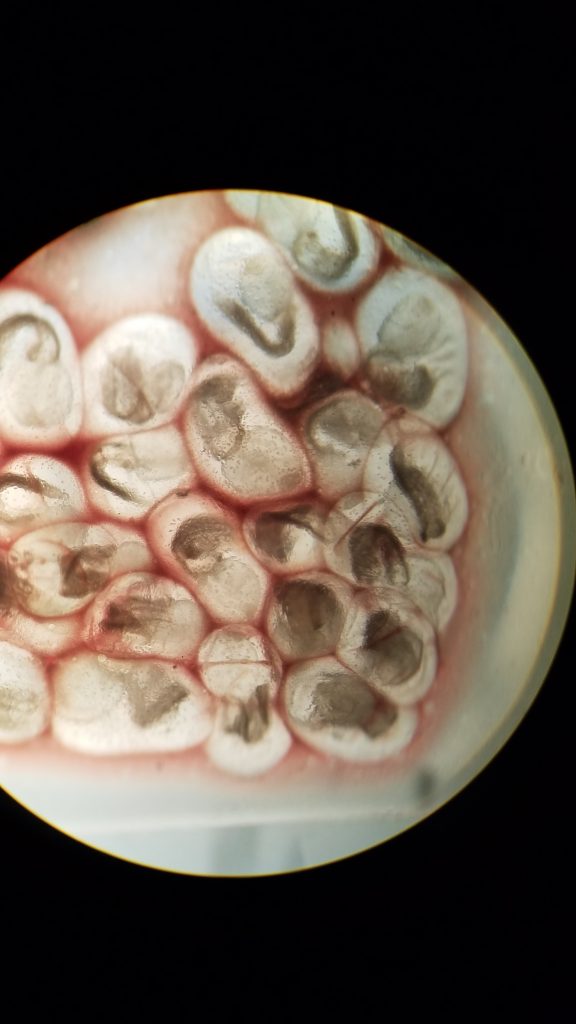
Large cluster of Liver Flukes visible to the naked eye: (from section 001F Spring 2019)
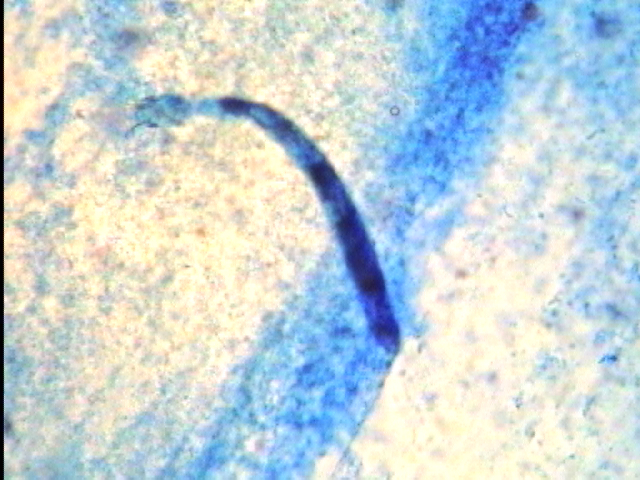
Nematode worm from fish intestines:
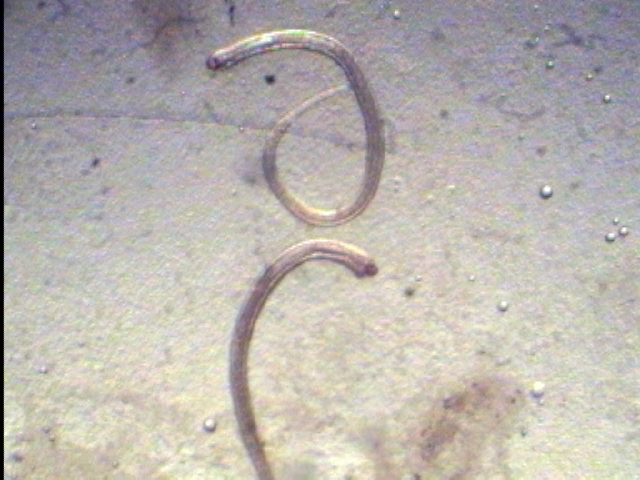

Acanthocephalus worm from fish mouth scraping: