Description
Bed bugs are parasites that feed on the blood of people, using these blood meals to grow and reproduce. They do not distinguish between dirty or clean homes and all people are vulnerable to infestations in their homes. Bedbugs are also capable of feeding on animals, including dogs, cats, and other pets.
They live close to areas where people typically sleep, rest, or sit for long periods. Hungry bugs will move out from their hiding places, in search of exposed skin. Typically, the head and neck are bitten, but bed bugs will also bite bare arms, hands, and legs. When searching for a place to feed, these bugs can move very quickly. Once an appropriate site is found, they feed for 2-5 minutes until full, and then move quickly away from the person and into a hiding place.
In addition to bed bugs moving towards a person when they are least likely to notice the insects, the result of their bites may also go unnoticed, or can be mistaken for the bites of other pests. All people are not equally sensitive to bed bug bites, so while some victims break out in rashes from the bites, other people may not display symptoms. When a reaction does occur, the results of feeding can be mild (a simple red spot) to severe (rash or even hives). The reactions caused by feeding might be mistaken for other problems. Fleas, mosquitoes and other biting insects, sensitization to detergents and soaps, and irritants (e.g., poison ivy) are some of the conditions victims of bed bugs thought they were dealing with.
Bed bugs are not known to transmit disease to people. They have been discovered to harbor 28 different human pathogens, but fortunately, the transmission of these diseases to people has not been demonstrated.
What they look like
Bed bugs are active at night and generally hide during the day. After mating, females lay white, oval eggs (1/16-inch long) into cracks and crevices. An individual bed bug can lay 200-250 eggs in her lifetime. The eggs hatch in about 6-10 days and the newly emerged bed bug nymphs seek a blood meal. Immature nymphs molt five times (i.e., they shed their outer exoskeleton in order to grow) before reaching adulthood. They need to feed at least once before each molt, although they could feed as often as once a day. There may be three or more generations per year. All ages are found in a reproducing population. Immature bed bugs may live for several months without feeding while adults may survive as long as one year without a meal. Under normal circumstances, adult bed bugs will live for about ten to eleven months.

Life Cycle
Bed bugs are active at night and generally hide during the day. After mating, females lay white, oval eggs (1/16-inch long) into cracks and crevices. An individual bed bug can lay 200-250 eggs in her lifetime. The eggs hatch in about 6-10 days and the newly emerged bed bug nymphs seek a blood meal. Immature nymphs molt five times (i.e., they shed their outer exoskeleton in order to grow) before reaching adulthood. They need to feed at least once before each molt, although they could feed as often as once a day. There may be three or more generations per year. All ages are found in a reproducing population. Immature bed bugs may live for several months without feeding while adults may survive as long as one year without a meal. Under normal circumstances, adult bed bugs will live for about ten to eleven months.
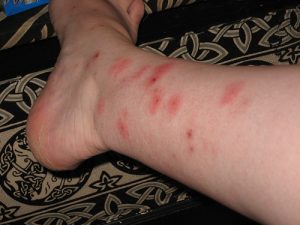
How to detect infestation
- Rusty or reddish stains on bed sheets or mattresses caused by bed bugs being crushed.
- Dark spots (about this size: •), which are bed bug excrement and may bleed on the fabric like a marker would.
- Eggs and eggshells, which are tiny (about 1mm) and pale yellow skins that nymphs shed as they grow larger.
- Live bed bugs.
Where Bed Bugs Hide

When not feeding, bed bugs hide in a variety of places. Around the bed, they can be found near the piping, seams and tags of the mattress and box spring, and in cracks on the bed frame and headboard. If the room is heavily infested, you may find bed bugs:
- In the seams of chairs and couches, between cushions, in the folds of curtains.
- In drawer joints.
- In electrical receptacles and appliances.
- Under loose wall paper and wall hangings.
- At the junction where the wall and the ceiling meet.
- Even in the head of a screw.
Since bed bugs are only about the width of a credit card, they can squeeze into really small hiding spots. If a crack will hold a credit card, it could hide a bed bug.
Are you planning to travel? Check out the Bed Bug Registry before you stay at a hotel (click on Look Up + Report).